RNN

递归神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network, RNN)是一种专门处理序列的神经网络。它们通常用于自然语言处理(NLP) 任务,因为RNN在处理文本方面非常有效。
第一句话:我喜欢吃苹果!
第二句话:苹果真是一家很棒的公司!
如果任务是要给苹果打标签,RNN就结合上下文去训练模型,能够准确识别出第一个苹果是一种水果,第二个是苹果公司,
RNN能够将可变长度序列作为输入和输出
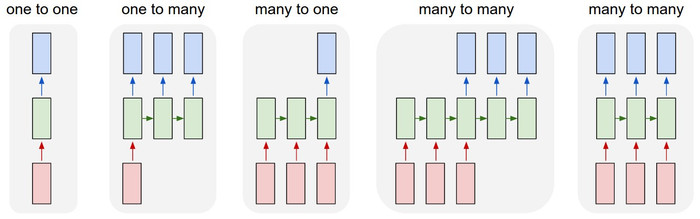
- 固定大小的输入到固定大小的输出(例如图像分类)。
- 序列输出(例如,从图像字幕生成)。
- 序列输入(例如,句子情感分析)。
- 序列输入和序列输出(例如机器翻译)。
- 同步序列输入和输出(例如,视频分类)
实现过程
正向传播:
如果使用一个“多对一”的RNN,来进行情感分析,即输入词向量属于正向\负向情感的概率
如下图:

RNN的计算遵循如下规则:
-
下一个隐藏状态是使用上一个隐藏状态和下一个输入决定的
,式子中使用了tanh作为激活函数
-
输出向量y由h所决定
其中,为用来链接**的权重,用来链接的权重,用来链接** 的权重,
的偏差,用来链接 的偏差
反向传播
训练RNN权重参数,首先需要一个损失函数。通常使用Softmax与交叉熵损失函数,作为损失函数。
将L对y进行求导:
例如,如 softmax(y) = [0.2,0.2,0.6],正确的类别为 0 ,那么对L求导得到:[-0.8, 0.2, 0.6]
再将L分别对RNN中所有参数进行求导:
因为变化会影响每一个,这都会影响最终的损失函数,因此我们需要将每个时间的梯度都计算出来然后加起来,作为每次更新的梯度值,这称为时序反向传播算法(BPTT)

同样得到:
联合①⑤⑧得到
联合①⑥⑧得到
联合①⑦⑧得到
梯度下降
计算完所有梯度后,使用梯度下降来更新权重和偏差。
代码
# This is a simple demo for using RNN to predict the phrases sentiment in the dataset.
import numpy as np
from database import test_data, train_data
from numpy import random
'''
Dimension of vector:
h=[64,1]
why[2,64]
whh[64,64]
wxh[2,64]
bh[64,1]
by[2,1]
y=[2,1]
'''
class RNN:
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, hidden_size=64):
# Define hidden layer has 64 neurons
self.Whh = random.randn(hidden_size, hidden_size) / 1000
self.Wxh = random.randn(hidden_size, input_size) / 1000
self.Why = random.randn(output_size, hidden_size) / 1000
self.bh = np.zeros((hidden_size, 1))
self.by = np.zeros((output_size, 1))
self.last_hs = {}
self.last_inputs = []
def forward(self, inputs):
h = np.zeros((self.Whh.shape[0], 1))
self.last_inputs = inputs
self.last_hs = {0: h}
for i, x in enumerate(inputs):
h = np.tanh(self.Wxh @ x + self.Whh @ h + self.bh)
self.last_hs[i + 1] = h
# enumerate:枚举 @:矩阵的乘法
y = self.Why @ h + self.by
return y
def backprop(self, d_y, learn_rate=2e-2):
n = len(self.last_inputs)
d_Why = d_y @ self.last_hs[n].T
d_Whh = np.zeros(self.Whh.shape)
d_Wxh = np.zeros(self.Wxh.shape)
d_bh = np.zeros(self.bh.shape)
d_by = d_y
# Calculate dL/dh for the last h.
d_h = self.Why.T @ d_y
for t in reversed(range(n)):
temp = ((1 - self.last_hs[t + 1] ** 2) * d_h)
d_bh += temp
d_Whh += temp @ self.last_hs[t].T
d_Wxh += temp @ self.last_inputs[t].T
d_h = self.Whh @ temp
# Make the values between -1 and 1
for d in [d_Wxh, d_Whh, d_Why, d_bh, d_by]:
np.clip(d, -1, 1, out=d)
# Using gradient descent to update the weights and biases
self.Whh -= learn_rate * d_Whh
self.Wxh -= learn_rate * d_Wxh
self.Why -= learn_rate * d_Why
self.bh -= learn_rate * d_bh
self.by -= learn_rate * d_by
def softMax(x):
return np.exp(x) / sum(np.exp(x))
def createInputs(text):
# Returns one-hot vectors representing the words in the input text
inputs = []
for w in text.split(' '):
v = np.zeros((vocab_size, 1))
v[word_to_idx[w]] = 1
inputs.append(v)
return inputs
def processData(data, backprop=True):
items = list(data.items())
random.shuffle(items) # shuffle:random arrangement the order of the list
loss = 0
num_correct = 0
for x, y in items:
inputs = createInputs(x)
target = int(y)
out = rnn.forward(inputs)
prob = softMax(out)
loss += (-np.log(prob[target]))
num_correct += int(np.argmax(prob) == target) # argmax :index of the max value
if backprop:
# get DL\Dy
d_y = prob
d_y[target] -= 1
rnn.backprop(d_y)
return loss / len(data), num_correct / len(data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Generate "one-hot" word vector
vocab = list(set([w for text in train_data.keys() for w in text.split(' ')]))
vocab_size = len(vocab)
word_to_idx = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(vocab)}
idx_to_word = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(vocab)}
# Generate rnn
rnn = RNN(input_size=len(vocab), output_size=2)
print("负情感" if np.argmax(softMax(rnn.forward(createInputs("i am not earlier")))) == 0 else "正情感")
for epoch in range(1000):
train_loss, train_acc = processData(train_data)
if epoch % 100 == 99:
print(f'--- Epoch {epoch + 1}')
print(f'Train Loss: {np.round(train_loss, 3)} | Accuracy: {np.round(train_acc, 3)}')
test_loss, test_acc = processData(test_data, backprop=False)
print(f'Test Loss: {np.round(test_loss, 3)} | Accuracy: {np.round(test_acc, 3)}')
print("负情感"if np.argmax(softMax(rnn.forward(createInputs("i am not earlier"))))==0 else "正情感")
简单的数据集:
train_data = {
'good': True,
'bad': False,
'happy': True,
'sad': False,
'not good': False,
'not bad': True,
'not happy': False,
'not sad': True,
'very good': True,
'very bad': False,
'very happy': True,
'very sad': False,
'i am happy': True,
'this is good': True,
'i am bad': False,
'this is bad': False,
'i am sad': False,
'this is sad': False,
'i am not happy': False,
'this is not good': False,
'i am not bad': True,
'this is not sad': True,
'i am very happy': True,
'this is very good': True,
'i am very bad': False,
'this is very sad': False,
'this is very happy': True,
'i am good not bad': True,
'this is good not bad': True,
'i am bad not good': False,
'i am good and happy': True,
'this is not good and not happy': False,
'i am not at all good': False,
'i am not at all bad': True,
'i am not at all happy': False,
'this is not at all sad': True,
'this is not at all happy': False,
'i am good right now': True,
'i am bad right now': False,
'this is bad right now': False,
'i am sad right now': False,
'i was good earlier': True,
'i was happy earlier': True,
'i was bad earlier': False,
'i was sad earlier': False,
'i am very bad right now': False,
'this is very good right now': True,
'this is very sad right now': False,
'this was bad earlier': False,
'this was very good earlier': True,
'this was very bad earlier': False,
'this was very happy earlier': True,
'this was very sad earlier': False,
'i was good and not bad earlier': True,
'i was not good and not happy earlier': False,
'i am not at all bad or sad right now': True,
'i am not at all good or happy right now': False,
'this was not happy and not good earlier': False,
}
test_data = {
'this is happy': True,
'i am good': True,
'this is not happy': False,
'i am not good': False,
'this is not bad': True,
'i am not sad': True,
'i am very good': True,
'this is very bad': False,
'i am very sad': False,
'this is bad not good': False,
'this is good and happy': True,
'i am not good and not happy': False,
'i am not at all sad': True,
'this is not at all good': False,
'this is not at all bad': True,
'this is good right now': True,
'this is sad right now': False,
'this is very bad right now': False,
'this was good earlier': True,
'i was not happy and not good earlier': False,
}
运行结果
正情感
--- Epoch 100
Train Loss: [0.688] | Accuracy: 0.552
Test Loss: [0.699] | Accuracy: 0.5
...
--- Epoch 1000
Train Loss: [0.002] | Accuracy: 1.0
Test Loss: [0.004] | Accuracy: 1.0
负情感
在训练了1000代后,能够正确的预测结果了